- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- hawaiian
- Hindi
- Hungarian
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Lao
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Maltese
- Myanmar
- Norwegian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Romanian
- Russian
- Serbian
- Slovak
- Somali
- Spanish
- Swedish
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Vietnamese
GET A QUOTE
Feb . 10, 2025 11:08 Back to list
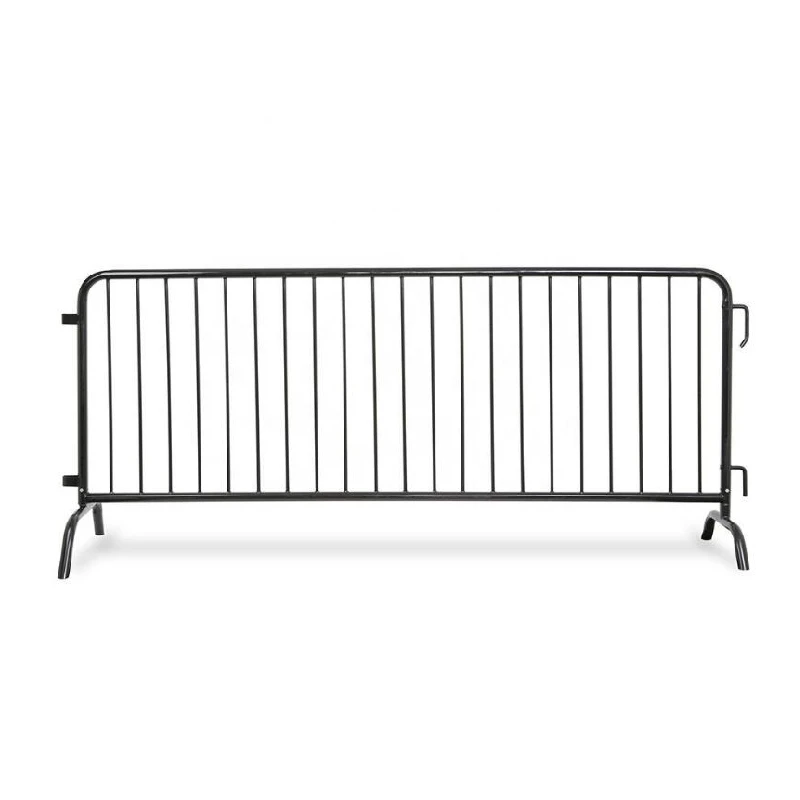
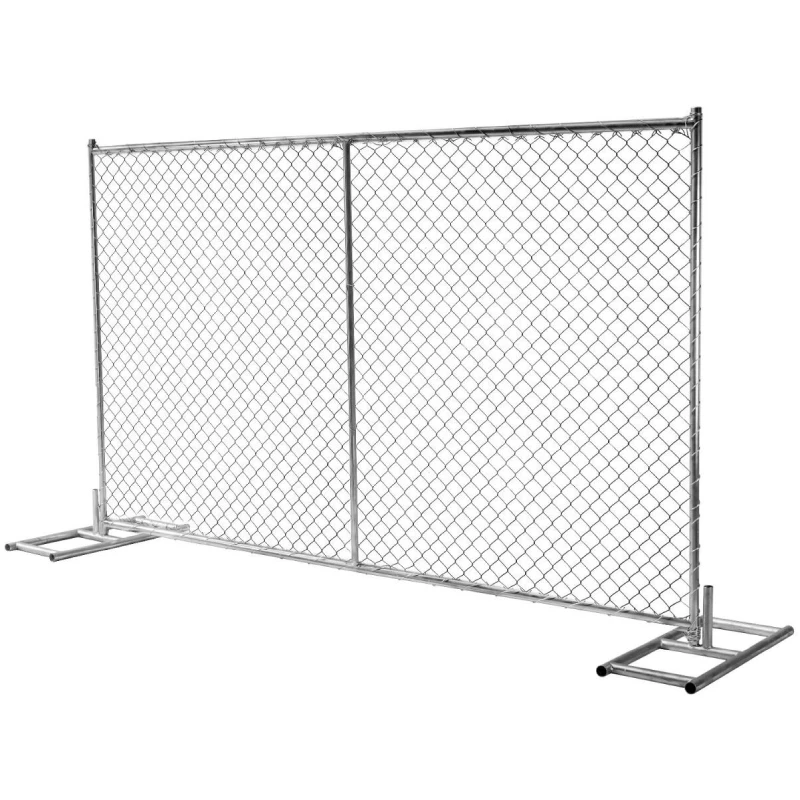
movable livestock fencing
Movable livestock fencing stands at the intersection of innovation and necessity, revolutionizing how farmers and ranchers manage their livestock. The demands of contemporary agriculture necessitate modular solutions that enhance efficiency while fostering animal welfare. As a seasoned expert in agricultural practices, I aim to delve into the multifaceted benefits and features of movable livestock fencing, subtly crafting an informative narrative that highlights both its utility and intrinsic value.
Authority in the field of movable livestock fencing can be attributed to numerous institutions and studies that advocate for its use. Research from agricultural universities consistently demonstrates the economic and environmental benefits of these systems. By reducing overgrazing, improving pasture regrowth, and enhancing soil conditions, movable fencing supports sustainable farming practices, earning validation from both environmental experts and agricultural engineers. Trustworthiness in movable livestock fencing is established through consistent performance and the tangible advantages outlined by users globally. Testimonials from farmers who have switched from conventional to movable systems frequently cite increased operational efficiency and livestock health improvements. This credibility is further reinforced by industry publications and endorsements from agricultural cooperatives. In examining the transformative potential of movable livestock fencing, one must consider its role within the broader tapestry of modern agriculture. As farmers face unpredictable weather patterns and fluctuating market demands, systems that afford flexibility and resilience are indispensable. Movable fencing meets this need by offering a scalable, adaptable solution that aligns with the principles of responsible land stewardship and animal care. In conclusion, the pivot to movable livestock fencing signifies more than just an operational upgrade; it represents a forward-thinking strategy that synthesizes technology, animal welfare, and environmental stewardship. The seamless integration of these systems into everyday agricultural practice exemplifies a shift towards a more sustainable, efficient future. As such, movable livestock fencing is not only a practical investment for farmers but also a critical component of ethical and sustainable food production worldwide.


Authority in the field of movable livestock fencing can be attributed to numerous institutions and studies that advocate for its use. Research from agricultural universities consistently demonstrates the economic and environmental benefits of these systems. By reducing overgrazing, improving pasture regrowth, and enhancing soil conditions, movable fencing supports sustainable farming practices, earning validation from both environmental experts and agricultural engineers. Trustworthiness in movable livestock fencing is established through consistent performance and the tangible advantages outlined by users globally. Testimonials from farmers who have switched from conventional to movable systems frequently cite increased operational efficiency and livestock health improvements. This credibility is further reinforced by industry publications and endorsements from agricultural cooperatives. In examining the transformative potential of movable livestock fencing, one must consider its role within the broader tapestry of modern agriculture. As farmers face unpredictable weather patterns and fluctuating market demands, systems that afford flexibility and resilience are indispensable. Movable fencing meets this need by offering a scalable, adaptable solution that aligns with the principles of responsible land stewardship and animal care. In conclusion, the pivot to movable livestock fencing signifies more than just an operational upgrade; it represents a forward-thinking strategy that synthesizes technology, animal welfare, and environmental stewardship. The seamless integration of these systems into everyday agricultural practice exemplifies a shift towards a more sustainable, efficient future. As such, movable livestock fencing is not only a practical investment for farmers but also a critical component of ethical and sustainable food production worldwide.
Prev:
Next:
Latest News
-
The Vital Role of Wire Mesh in Construction
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Essential Benefits of Welded Wire Mesh
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Secure Your Property with Field Farm Fence
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Expert Chain Link Fence Installation
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Discover the Versatility of Hexagonal Wire Mesh
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Barbed Wire
NewsJul.01,2025
Related Products