- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- hawaiian
- Hindi
- Hungarian
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Lao
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Maltese
- Myanmar
- Norwegian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Romanian
- Russian
- Serbian
- Slovak
- Somali
- Spanish
- Swedish
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Vietnamese
Dek . 04, 2024 10:34 Back to list
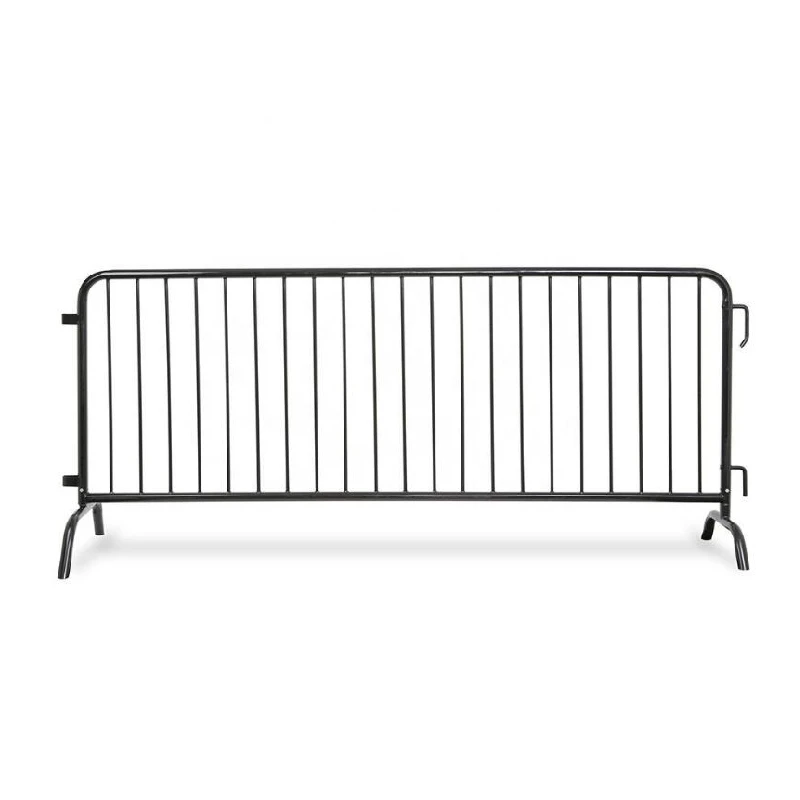
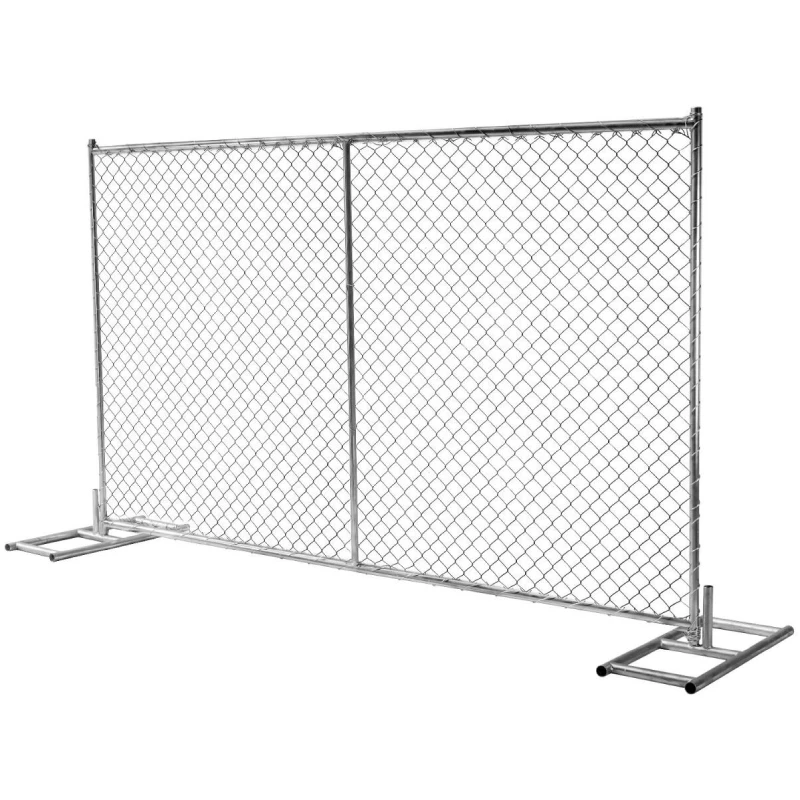
control barriers
Understanding Control Barriers A Key to Safety and Efficiency
Control barriers play a crucial role in various sectors, including manufacturing, transportation, and information technology, by establishing limits and protocols to enhance safety and operational efficiency. These barriers are designed to prevent accidents, mitigate risks, and control the flow of processes, ensuring that activities meet regulatory standards and organizational goals.
Definition and Importance
Control barriers can be defined as mechanisms or systems that create boundaries around processes, equipment, or information. They act as safeguards to limit exposure to hazards and prevent undesirable events from occurring. In a manufacturing environment, for instance, control barriers might include safety guards on machines, emergency stop buttons, or automated shutdown systems. In the realm of cybersecurity, they can manifest as firewalls, encryption protocols, and access controls that protect critical data from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
The importance of these barriers cannot be overstated. They serve to protect employees, customers, and the environment from detrimental impacts. By clearly delineating safe operating procedures and emergency protocols, organizations can enhance their overall safety culture while simultaneously ensuring regulatory compliance. Moreover, effective control barriers can lead to improved operational efficiency by minimizing downtime and reducing the chance of catastrophic failures that might disrupt production.
Types of Control Barriers
Control barriers can be classified into several categories, each serving different functions and addressing various risks
1. Physical Barriers These include fences, walls, or safety enclosures designed to physically separate hazardous areas from safe zones. In industrial settings, these barriers are essential for protecting workers from dangerous machinery.
2. Administrative Barriers These encompass policies, procedures, and training programs that govern how tasks should be performed. For example, proper training in handling hazardous materials is an essential administrative control that reduces risks in workplaces dealing with dangerous substances.
control barriers

3. Technological Barriers Technological controls employ software or automated systems to monitor and manage risks. An example is an automated alert system that notifies personnel of equipment malfunctions or environmental hazards in real time.
4. Behavioral Barriers These focus on creating a culture of safety among employees. Behavioral barriers involve training and engagement programs where employees are empowered to recognize and report unsafe practices or conditions.
Implementing Effective Control Barriers
To effectively implement control barriers, organizations must first conduct a comprehensive risk assessment. This assessment identifies potential hazards and evaluates existing controls' effectiveness. Based on the findings, organizations can prioritize which barriers need to be developed or reinforced.
Next, training and communication are paramount. Employees must understand not just the existence of control barriers but also their purpose and proper use. Regular drills and training sessions can help engrain these practices in the organizational culture.
Engineering and technological solutions should also be leveraged to provide additional layers of protection. Investing in advanced monitoring systems and automation can greatly reduce human error, which is often a significant factor in accidents.
Conclusion
In conclusion, control barriers are essential for fostering a safe and efficient working environment. By understanding their types and functions and committing to their proper implementation, organizations can significantly reduce risks associated with operations while promoting a culture of safety. As industries continue to evolve, ongoing assessments and updates to these control mechanisms will be vital in ensuring they remain effective against emerging challenges. By prioritizing control barriers, organizations can not only protect their workforce and assets but also enhance productivity and trust among stakeholders.
-
Your Ultimate Solution for Australian Temporary Fencing
NewsMay.14,2025
-
The Ultimate Guide to Crowd Control Barriers: Secure Your Events with Ease
NewsMay.14,2025
-
Secure Your Livestock with High-Quality Livestock Fence Panels
NewsMay.14,2025
-
Enhance Your Livestock Management with Top-Quality Cattle Fences
NewsMay.14,2025
-
Enhance Security and Safety with Temporary Fencing Solutions
NewsMay.14,2025
-
Corral Gates
NewsMay.14,2025